Key Business Implications of the Healthcare Services Act (HCSA)
By Medinex Team
Sept 23, 2025
By Medinex Team
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Understanding The Licensing and Governance Requirements For Your Private Practice
2. What is Licensable Healthcare Services (LHS)?
Under the HCSA, specific healthcare services are required to obtain a license in order to operate legally. On top of getting the licences for the Licensable Healthcare Services (LHS) that you intend to provide, you must also secure the relevant Mode of Service Delivery (MOSD) applicable for your LHS. This is a change from the PHMCA, where providers were licensed based only on physical premises.
What Are The Licensable Healthcare Services?
• Acute Hospital Service
• Ambulatory Surgical Centre Service
• Assisted Reproduction Service
• Blood Banking Service
• Clinical Laboratory Service
• Community Hospital Service
• Cord Blood Banking Service
• Emergency Ambulance Service
• Medical Transport Service
• Human Tissue Banking Service
• Nuclear Medicine Service
• Nursing Home Service
• Outpatient Dental Service
• Outpatient Medical Service
• Outpatient Renal Dialysis Service
• Radiological Service
3. What Are The Different Modes of Service Delivery (MOSD)?
MOH defines the allowable MOSDs you can choose from for each LHS. Refer to the diagram and example below for a better understanding of the 4 modes of service delivery and their implications.
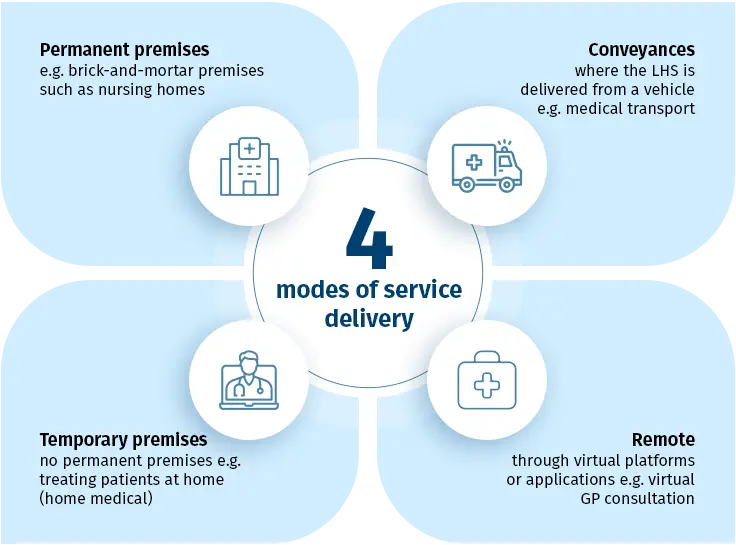
Example
Dr John Lee wants to set up a private clinic that offers both medical and dental services in Singapore. For the Outpatient Medical Service, on top of the medical services offered by his clinic, he also wanted to offer teleconsultation by his team of doctors to cater to the needs of different groups of patients.
What are the licenses Dr John needs to hold?
An Outpatient Medical Service licence approved for the following MOSDs:
• Permanent premises
• Remote delivery
• Permanent premises
4. What Specified Services Require MOH Approval?
Complex or higher risk procedures provided in a LHS may be categorised as Specified Services (SSes) as they have distinct requirements for patient safety. You will need to seek MOH’s approval before the commencement of these Specified Services under your LHS. It is an offence to offer any Specified Services without securing MOH’s approval.
Here are some examples of the specialised procedures that are considered Specified Services.
• Radiation oncology
• Endoscopy
• Liposuction
• Dental cone beam computed tomography
5. Governance Requirements For Your Healthcare Services
Besides the Licensing requirements, HCSA also refined roles and responsibilities of key personnels in order to strengthen the governance and oversight of the Licensed Healthcare Service. In addition to the licensee, roles such as Key Appointment Holder (KAH) and the Principal Officer (PO) are formalised. The appointment of the Clinical Governance Officer (CGO) is also added. Each of these roles has specific responsibilities and code of practice.
An Overview of the Key Personnel's Responsibilities
- Licensee (Individual/Corporation): Responsible and accountable for overall compliance with HCSA. Appointment of suitable individuals for other key roles.
- Key Appointment Holder (Individual(s)): Responsible for strategic leadership and general management oversight.
- Clinical Governance Office (Individual (Clinical & Technical expert): Assists the licensee in clinical governance and technical oversight of complex services.
- Principal Officer (Individual): Assists the licensee in ensuring overall compliance with HCSA. Oversees day-to-day management of the service.
For larger healthcare service providers with ample manpower resources, appointing qualified and suitable individuals to fulfil the different roles may be more manageable when compared to a smaller set-up like General Practitioner (GP) or Specialist clinic. For them, the physician who owns and runs the clinic may end up taking on all or multiple roles. These additional roles may prevent them from dedicating more attention to patient care and business growth.
With these additional responsibilities, the time and resource crunch may become stumbling blocks for these medical practices or healthcare businesses. To overcome these challenges, they can consider strengthening two key areas of their private practices or healthcare businesses.
- Effective Clinic Operations: They can consider upgrading to a new integrated system that will help streamline data management and communication, optimise scheduling systems, patient flow and more. These solutions automate labourious manual processes and reduce human errors. Not only will they have better clarity of their operations, they will also be able to manage their clinics or healthcare businesses with greater efficiency.
- Building Stronger Competencies: They can invest in training their clinic staff to equip them with the right skills to handle their specific roles competently. A well-trained clinic manager can relieve doctors of operational responsibilities, allowing them to focus on more important areas of their private practices or healthcare businesses.
